The following newsletter provides highlights from the ViralEd program "HIV Treatment and Prevention: How to Recognize and Address Health Care Disparities and Improve Treatment Outcomes." To watch the CME videos of HIV experts discussing these issues in depth, please go to this link:

HIV Risk Highest in Black and Hispanic Males
HIV diagnosis, mortality, and census population data were used to derive lifetime risk estimates of HIV diagnosis for all ages, by sex, race/ethnicity, and place of residence. Based on 2017-2019 U.S. data, the lifetime risk of an HIV diagnosis was 1 in 120 overall: 1 in 76 for males and 1 in 309 for females. Lifetime risk for males was 1 in 27 for black persons, 1 in 50 for Hispanic persons, 1 in 89 for Native Hawaiian/other Pacific Islander persons, 1 in 116 for American Indian/Alaska Native persons, 1 in 171 for white persons, and 1 in 187 for Asian persons; and for females was 1 in 75 for black persons, 1 in 287 for Hispanic persons, 1 in 435 for American Indian/Alaska Native persons, 1 in 611 for Native Hawaiian/other Pacific Islander persons, 1 in 874 for white persons and 1,298 for Asian persons. By jurisdiction, the lifetime risk ranged from 1 in 39 in Washington, DC to 1 in 655 in Wyoming. The states with the highest lifetime risks were Georgia (1 in 59), Florida (1 in 63), Louisiana (1 in 69), Nevada (1 in 84) and Maryland (1 in 85).
Source: Singh S, Hu X, Hess K, et al. Estimating the lifetime risk of a diagnosis of HIV infection in the United States. 2022 CROI, February 12-16 and 22-24, 2022. Abstract 43.
Long-acting Cabotegravir: Safe and Effective in Preventing HIV Infection in Cisgender Women
Delany-Moretlwe and colleagues compared the safety and efficacy of long-acting injectable cabotegravir (CAB) with daily, oral TDF/FTC for HIV prevention in cisgender women. HIV-uninfected PrEP eligible cisgender women were randomized 1:1 to either active CAB plus TDF/FTC placebo or active TDF/FTC plus CAB placebo. Participants were enrolled at sites in South Africa, Zimbabwe, Uganda, Malawi, Botswana, Eswatini, and Kenya. Forty incident infections were observed over 3,892 person-years: four in the CAB arm and 34 in the TDF/FTC arm. The investigators concluded that both products demonstrated high prevention efficacy and were safe and well-tolerated, but CAB was superior to TDF/FTC in preventing HIV infection in cisgender women. They noted that CAB LA likely provided an adherence advantage over daily TDF/FTC. Ongoing testing is being undertaken to understand the reasons for breakthrough infections.
Source: Delany-Moretlwe S, Hughes J, Bock P, et al. Long acting injectable cabotegravir is safe and effective in preventing HIV infection in cisgender women: interim results from HPTN 084. HIV R4P/Virtual. January 27-28, February 3-4, 2021; Abstract HY01.02LB.
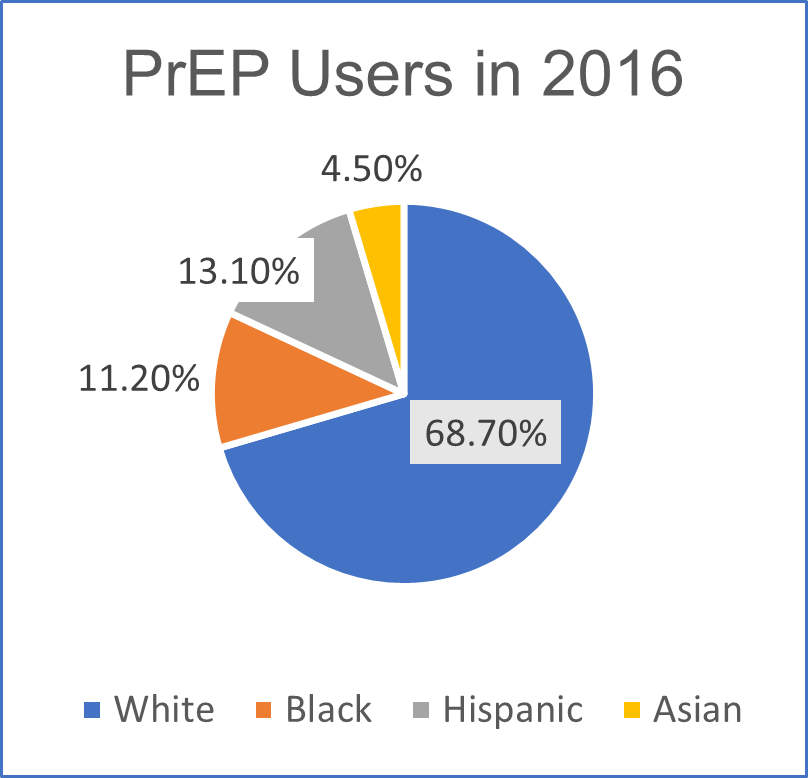
Disparities in PrEP Implementation Found by Race and Sex
The CDC reported that 1.1 million people are at risk of acquiring HIV infection and have indications for PrEP. Of these individuals, 26.3% are white, 43.7% are black, and 24.7% are Hispanic. In 2016, among 32,853 (41.9%) PrEP users for whom race/ethnicity data were available, 68.7% were white, 11.2% were black, 13.1% were Hispanic, and 4.5% were Asian (Figure). Approximately 7% of people who had indications for PrEP were prescribed PrEP in 2016, including 2.1% of women with PrEP indications. Despite the availability of PrEP since 2012, disparities in uptake persist. Although black men and women accounted for approximately 40% of persons with PrEP indications, nearly six times as many white men and women were prescribed PrEP as were black men and women. The findings of this study highlight gaps in effective PrEP implementation efforts in the United States.
Source: Huang YA, Zhu W, Smith DK, et al. HIV Pre-exposure Prophylaxis, by Race and Ethnicity - United States, 2014-2016. MMWR. 2018;67:1147-50. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 2021. HIV National Strategic Plan for the United States: A Roadmap to End the Epidemic 2021-2025. Washington, DC.
Figure: PrEP users for whom race/ethnicity data were available.
Black Women May Underestimate HIV Risk, Affecting Testing and PrEP Use
In a population of Philadelphia, PA residents testing for HIV, of whom more than 90% were black, 56.8% of men reported a moderate-high risk, while only 8.3% of women believed their risk to be moderate-high. In the National Survey on HIV in the Black Community (NSHBC) - a cross-sectional survey of black people ages 18-50 in United States - the most common reason for declining PrEP use was low-risk perception. To improve PrEP uptake, interventions to increase risk awareness, PrEP knowledge, and access to care are needed.
Sources: Kwakwa HA, Bessias S, Sturgis D, et al. Attitudes Toward HIV Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis in a United States Urban Clinic Population. AIDS Behav. 2016;20:1443-50. Ojikutu BO, Bogart LM, Higgin-Biddle M, et al. AIDS Behav. 2018;22:3576-87.
HPTN 083 - Updated Results Reported
The HPTN 083 study reported a 66% reduced risk of HIV acquisition for those taking long-acting injectable cabotegravir (CAB) compared with those taking daily oral tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine (TDF/FTC) in the prespecified primary analysis. The study was unblinded in May 2020 and participants continued their study treatment. Fifty-one incident HIV infections were identified in the blinded trial (12 CAB, 39 TDF/FTC). The investigators recently reported updated HIV incidence rates in both study arms during the blinded phase of the trial, plus after one year of follow-up: they identified 46 additional incident HIV infections in the pre-planned analysis period (13 CAB, 33 TDF/FTC). Of these infections, four occurred during the blinded phase (two CAB, two TDF/FTC), and 42 after unblinding (11 CAB, 31 TDF/FTC). The reduction in risk of HIV acquisition for CAB vs. FTC/TDF remained similar in blinded and unblinded phases [HR=0.33 95% CI (0.18-0.62) and HR=0.34 95% CI (0.17-0.67)]. The two newly-identified blinded CAB arm infections were both in the setting of on-time injections; the 11 newly-identified unblinded CAB arm infections included one with on-time injections, three with delayed injections, and seven that occurred ≥6 months after the final CAB treatment (two of these seven never received a CAB injection). Six additional new CAB arm infections were identified after ≥3 years on study (all ≥6 months after the final CAB exposure). The investigators stated that HIV incidence was higher in both arms in the unblinded phase, which was likely attributable to decreased TDF/FTC adherence, reduced CAB injection coverage, and increased relative contributions to overall person-time from high incidence regions. These findings demonstrated that the relative reduction in HIV incidence for CAB compared to daily oral FTC/TDF was consistent during one year of additional unblinded study follow-up.
Source: Landovitz R, Donnell D, Tran H, et al. Updated efficacy, safety, and case studies in HPTN 083: CAB-LA vs TDF/FTC for PrEP. CROI 2022; February 12-16, 2022. Abstract 96.
Investigating the Impact of Long-Term Daily PrEP on Bone Mineral Density and Renal Function
Tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) shows high antiviral efficacy and improved renal and bone safety compared with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) when used for HIV treatment. Investigators from the DISCOVER trial reported primary results from a blinded phase 3 study evaluating the efficacy and safety of PrEP with TAF plus emtricitabine (FTC) vs. TDF plus FTC for HIV prevention. The study enrolled men who have sex with men and transgender women who have sex with men, both with a high risk of acquiring HIV on the basis of their self-reported sexual behavior in the past 12 weeks or their recent history (within 24 weeks of enrollment) of bacterial sexually transmitted infections. The investigators reported that daily TAF/FTC showed non-inferior efficacy to daily TDF/FTC for HIV prevention. While the number of adverse events for both regimens was low, TAF/FTC had more favorable effects on bone mineral density and biomarkers of renal safety than TDF/FTC.
Source: Mayer KH, Molina J-M, Thompson MA, et al. Emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide vs emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (DISCOVER): primary results from a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, active-controlled, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2020;396:239-54.
Transgender Women Face Increased Risk from HIV Infection
Transgender women (TW) face an increased risk of acquiring HIV infection. An analysis of TW in low-income, middle-income, and high-income countries estimated the odds ratio for being infected with HIV in TW compared with all adults of reproductive age across 15 countries was 48.8 (95% CI 21.2-76.3) and did not differ for those in low-income and middle-income countries compared with those in high-income countries. Further, it has been reported that 26% of TW misuse drugs or alcohol to cope with discrimination they face due to gender identity or gender expression. These and other findings suggest that TW are at high risk for acquiring HIV and are in urgent need of prevention, treatment, and care services.
Sources: Baral SD, Poteat T, Strömdahl S, et al. Worldwide burden of HIV in transgender women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13:214-22. Grant JM, Mottet LA, Tanis J, et al. National Transgender Discrimination Survey Report on Health and Health Care. October 2010. https://cancer-network.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/National_Transgender_Discrimination_Survey_Report_on_health_and_health_care.pdf
Effect of PrEP on Feminizing Hormone Therapy in Transgender Women
Concerns about potential drug-drug interactions (DDI) between feminizing hormone therapy (FHT) and PrEP have hampered uptake and adherence of PrEP among some TW. To determine DDI between FHT and PrEP, Hiransuthikul and colleagues measured pharmacokinetic parameters of blood plasma tenofovir (TFV), estradiol (E2), and testosterone in 20 TW who had not received an orchiectomy and had not received injectable FHT within 6 months. FHT (estradiol valerate and cyproterone acetate) were prescribed to participants at baseline until week 5, and week 8 until the end of study. PrEP (TDF/FTC) was initiated at week 3 and continued without interruption. The study found lower plasma TFV exposure in the presence of FHT, but PrEP had no impact on E2 or testosterone levels. Prior studies did not demonstrate higher infection rates for transgender patients on hormones. Further studies are warranted to determine whether these reductions in TFV are clinically significant.
Source: Hiransuthikul A, Himmad K, Kerr S, et al. Drug-drug interactions between the use of feminizing hormone therapy and pre-exposure prophylaxis among transgender women: The iFACT study. AIDS 2018; Amsterdam, the Netherlands; July 23-27, 2018; Abstract TUPDX0107LB.
DISCOVER Study: TAF/FTC vs. TDF/FTC for PrEP in MSM and Transgender Women
- Week 96 Analysis
Earlier reports that compared TDF/FTC with TAF/FTC demonstrated noninferior efficacy for HIV prevention and improved bone mineral density (BMD) and renal safety biomarkers at week 48 with TAF/FTC. Investigators evaluated renal and lipid parameters and weight changes in participants on TAF/FTC or TDF/FTC through week 96. BMD was assessed in younger participants (age <25 years), who are still accruing bone mass. They also examined glomerular function, proteinuria, and biomarkers of proximal tubular injury in participants ≥50 years of age and in those with moderate renal impairment (eGFR 60 to <90 mL/min). Among 5,387 participants who were evaluated, TAF/FTC users were found to have significantly increased BMD, unlike those on TDF/FTC. Participants <25 years had greater declines in BMD on TDF/FTC, with a greater magnitude of difference between groups than those ≥25 years. Overall, TAF/FTC users had increases in eGFR and declines in UPCR and PTI biomarkers. Older participants on TDF/FTC had a greater magnitude of decline in eGFR and a greater increase in UPCR and PTI markers compared to younger TDF/FTC users. Participants with eGFR 60 to <90 mL/min had greater statistically significant changes in PTI markers, if on TDF, compared with those with eGFR ≥90 mL/min. Those on TAF/FTC had stable lipids through week 96, while those on TDF/FTC had decreases in lipids at week 96. Those on TDF/FTC had a smaller weight increase than those on TAF/FTC through week 96. Overall, those on TAF/FTC had increased BMD compared to declines in those on TDF/FTC, with more pronounced differences in younger participants. Older participants who were taking TDF/FTC and those with impaired renal function had more adverse impact on renal biomarkers. Lipid and weight changes were consistent with the known lipid-lowering and weight suppressive effects of TDF. The research team concluded that TAF/FTC is a safe, longer-term option for PrEP, with certain subgroups experiencing a greater magnitude of benefit in BMD and renal biomarkers.
Source: Ogbuagu O, Podzamczer D, Salazar LC, et al. Longer-term safety of TAF/FTC and TDF/FTC for HIV PrEP: DISCOVER Trial Week 96 Results. 27th CROI; Boston, MA; March 8-11, 2020. Abstract 92.
Long-Acting Injectable Implant Investigated for Prevention of HIV and Unplanned Pregnancy
Researchers are studying an injectable, long-acting, biodegradable, and removable in-situ forming implant (ISFI) for the prevention of HIV and unplanned pregnancy. In this study with mice, ISFIs were loaded with dolutegravir (DTG) or cabotegravir (CAB) and one of two contraceptives, etonogestrel (ENG) or medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA). A 90-day pharmacokinetic (PK) and safety study was conducted in female BALB/c mice with optimized ISFI formulations. Mice (n=12/group) were injected subcutaneously with 50 µL of MPT ISFI formulations; plasma samples were collected longitudinally to quantify drug concentration. At day 90, depots were removed to quantify residual drug. The investigators reported that plasma concentrations of CAB and DTG were well above their 4x PA-IC90 for 90 days, demonstrated zero-order release kinetics, and showed no differences in drug release when formulated with either hormone. Plasma concentrations of ENG and MPA were at, or above target levels based on their marketed products for 90 days and MPA demonstrated zero-order release kinetics. These results demonstrated (1) the ability to co-formulate an ARV (DTG or CAB) and contraceptive (ENG or MPA) in a single ISFI; (2) sustained and target drug release kinetics in vivo for 90 days; and (3) all formulations were safe and well-tolerated. Future studies include assessing PK and efficacy in non-human primates.
Source: Young I, Palleria A, Maturavongsadit A, et al. Long-Acting Injectable for Prevention of HIV and Unplanned Pregnancy. CROI 2022; February 12-16, 2022. Abstract 80.

 |
 |
This activity is supported by an independent educational grant from Gilead Sciences Medical Affairs
and Janssen Therapeutics, Division of Janssen Products, LP
|
CONTACT INFO
Unsubscribe from this list.
Contact Us by Email
Phone: 815-893-0768 | Fax: 917-591-6353
Copyright © 2022 | ViralEd, Inc. | All rights reserved.
|
